Can Liposculpture Cause Fat Embolism
Liposculpture, a popular cosmetic procedure, is often sought for its ability to reshape and contour the body. However, like any surgical procedure, it carries potential risks. Among these are fat embolism and pulmonary embolism, which can have serious health implications. This article delves into the relationship between liposculpture and these conditions, providing a comprehensive overview for those considering the procedure.
Understanding Fat Embolism and Pulmonary Embolism
Fat Embolism
Fat embolism occurs when fat droplets enter the bloodstream, potentially blocking blood vessels. This can happen during liposculpture when fat is dislodged and inadvertently enters the circulatory system. Symptoms may include respiratory distress, confusion, and a rash.
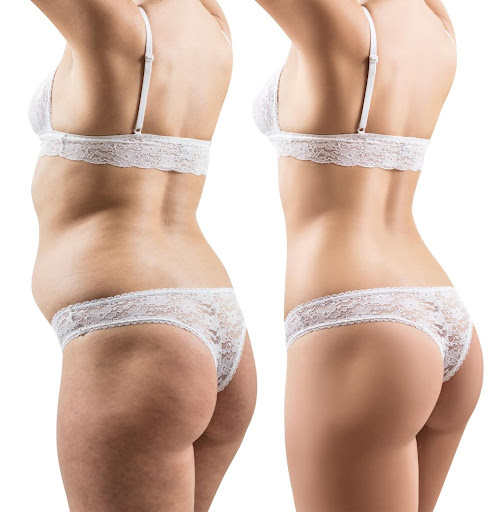
Liposculpture Slims Abdomen
Liposculpture Slims Abdomen by removing extra fat from the belly area using small tubes it helps people get a flatter tummy without big cuts or scars
Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism is a blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in the lungs, often caused by blood clots that travel from the legs or other parts of the body. In the context of liposculpture, fat embolism can lead to pulmonary embolism if fat droplets travel to the lungs.
- Fat embolism can cause serious complications if not addressed promptly.
- Pulmonary embolism is a life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical attention.
- Both conditions can arise as complications from liposculpture.
Liposculpture Procedure Overview
Tumescent Local Anesthesia Technique
The tumescent technique involves injecting a large volume of diluted local anesthetic into the subcutaneous fat. This method minimizes blood loss and provides anesthesia during the procedure. It is considered safer than general anesthesia and reduces recovery time.
Suction-Assisted Liposuction
Suction-assisted liposuction is the most common technique used in liposculpture. It involves using a cannula to suction out fat deposits. While effective, it requires precision to avoid complications such as fat embolism.
- Tumescent technique reduces the risk of bleeding and anesthesia-related complications.
- Suction-assisted liposuction is effective but requires skilled execution.
- Both techniques are integral to the liposculpture process.
Potential Complications of Liposculpture
Deep Venous Thrombosis
Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where blood clots form in deep veins, usually in the legs. It can occur after liposculpture due to prolonged immobility or other factors. DVT can lead to pulmonary embolism if clots travel to the lungs.
Systemic Effects
Systemic effects refer to complications that affect the entire body, such as fluid imbalance or infection. These can arise from the liposculpture procedure itself or from anesthesia.
- DVT is a serious risk that can lead to pulmonary embolism.
- Systemic effects can complicate recovery and require medical intervention.
- Awareness of these risks is crucial for patients considering liposculpture.
Fat Embolism Syndrome After Liposuction
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Fat embolism syndrome (FES) is characterized by a triad of symptoms: respiratory distress, neurological symptoms, and a petechial rash. Diagnosis is often clinical, supported by imaging and laboratory tests.
Treatment Options
Treatment for FES is primarily supportive, focusing on stabilizing the patient and addressing symptoms. This may include oxygen therapy, corticosteroids, and intensive care monitoring.
- FES symptoms can appear within 24-72 hours post-surgery.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for positive outcomes.
- Supportive care is the mainstay of FES management.
Pulmonary Embolism Following Liposculpture
Incidence Rates
The incidence of pulmonary embolism following liposculpture is relatively low but not negligible. It is essential for patients to be aware of this risk and discuss it with their surgeon.
Clinical Presentation
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood. These symptoms require immediate medical evaluation.
- Pulmonary embolism is a rare but serious complication of liposculpture.
- Awareness of symptoms can lead to prompt treatment and better outcomes.
- Discussing risks with a healthcare provider is crucial for informed decision-making.
Prevention Strategies
Patient Screening and Selection
Thorough patient screening can identify individuals at higher risk for complications. Factors such as age, medical history, and lifestyle should be considered.
Intraoperative Precautions
During the procedure, surgeons can take steps to minimize risks, such as using smaller cannulas and avoiding excessive fat removal.
- Proper patient selection reduces the risk of complications.
- Intraoperative precautions are essential for safe liposculpture.
- Communication between patient and surgeon is key to successful outcomes.
Diagnostic Measures for Fat and Pulmonary Embolism
Laboratory Tests
Blood tests can help identify markers of inflammation or clotting that may indicate embolism. These tests are part of a comprehensive diagnostic approach.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging, such as CT scans or MRIs, can visualize emboli in the lungs or other areas, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Laboratory tests provide valuable information for diagnosing embolism.
- Imaging techniques are crucial for confirming the presence of emboli.
- A combination of tests ensures accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Management of Embolism Complications
Acute Treatment Approaches
Acute management of embolism involves stabilizing the patient and addressing the underlying cause. This may include anticoagulants, oxygen therapy, and supportive care.
Long-Term Care and Follow-Up
Long-term management focuses on preventing recurrence and monitoring for complications. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential.
- Acute treatment aims to stabilize and treat the immediate threat.
- Long-term care involves prevention and monitoring for future risks.
- Ongoing communication with healthcare providers is vital for patient safety.
Expert Insights from Dr. Alexandre
Dr. Alexandre emphasizes the importance of safety protocols in liposculpture. He advocates for thorough patient education and informed consent, ensuring patients understand the risks and benefits of the procedure. His insights highlight the need for skilled practitioners and comprehensive patient care. Liposculpture vein impact can affect blood flow in treated areas This may cause temporary changes in how veins look under the skin Neuropathy liposculpture complications can cause numbness and pain in the treated areas This may lead to difficulty feeling or moving parts of the body after the procedure
Nerve complications liposculpture can cause numbness or tingling in the treated areas This may happen when nerves are accidentally damaged during the fat removal process Liposculpture contours physique is a way to shape the body by removing extra fat It helps create a smoother and more defined look in specific areas
Liposculpture motivates slimming by showing people how their body can look after fat removal This can inspire them to keep working on their fitness goals and maintain a healthier lifestyle Liposculpture fat removal is a way to shape your body by taking out extra fat It uses small tubes to suck out fat from specific areas to make you look slimmer
Liposculpture minimally tightens the skin by removing small amounts of fat from specific areas It can help shape the body but doesn’t significantly improve loose or sagging skin Liposculpture hepatic effects can impact the liver’s function and health This procedure may cause changes in how the liver processes fats and toxins
Liposculpture menstrual impact Liposuction alternative comparison Non-surgical fat reduction methods like coolsculpting and laser treatments offer less invasive options compared to traditional liposuction for those looking to slim down specific body areas Nano fat grafting pricing Dubai can vary depending on the clinic and doctor you choose People interested in this procedure should contact different clinics in Dubai to get specific price quotes for
Nil body contouring is a way to shape your body without doing anything It’s like magic that changes how you look but doesn’t actually do anything Emirati body contouring is a popular beauty treatment in the United Arab Emirates that helps people reshape their bodies
Advances in Liposculpture Techniques
Ultrasound-Guided Procedures
Ultrasound guidance enhances precision in liposculpture, reducing the risk of complications. This technology allows for more accurate fat removal and improved patient outcomes.
Energy-Based Liposuction Methods
Energy-based methods, such as laser or ultrasound-assisted liposuction, offer additional benefits by tightening the skin and reducing recovery time. These advances contribute to safer and more effective liposculpture.
- Ultrasound guidance improves precision and safety in liposculpture.
- Energy-based methods offer additional benefits and faster recovery.
- Technological advances continue to enhance liposculpture outcomes.
FAQ’s
Can Liposculpture Cause Blood Clots?
Liposculpture can increase the risk of blood clots, particularly in patients with predisposing factors. Clots can lead to serious complications like pulmonary embolism. Patients should discuss their risk factors with their surgeon and follow postoperative care instructions to minimize this risk.
How Long After Liposculpture Can a Fat Embolism Occur?
Fat embolism can occur within hours to days after liposculpture, typically within 24-72 hours. Patients should be vigilant for symptoms during this period and seek medical attention if they experience any concerning signs.
Is Liposculpture Safer Than Traditional Liposuction?
Liposculpture is often considered safer than traditional liposuction due to its precision and use of local anesthesia. However, both procedures carry risks, and safety depends on the surgeon’s skill and patient factors. Patients should discuss the pros and cons with their healthcare provider to make an informed choice.