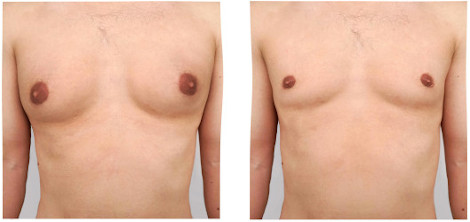
Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is a medical term meaning male breast enlargement. In the majority of cases there is no known cause and, although rarely talked about, it is a common condition. It may result from hormonal changes, heredity, disease, or the use of certain drugs, and can present unilaterally (one breast) or bilaterally (both breasts).
Most teenage boys experience some degree of breast enlargement affecting one or both breasts. However, by early adulthood less than 10% have a residual problem. This incidence rises with age, reaching approximately 30% (1 in 3) in older men.
Gynecomastia surgery is a procedure to remove excess fat, glandular tissue and/or skin from overdeveloped or enlarged male breasts. In severe cases of gynecomastia, the weight of excess breast tissue may cause the breasts to sag and stretch the areola (the dark skin surrounding the nipple). In these cases, the position and size of the areola can be surgically improved and excess skin may need to be reduced, leading to additional scarring.
For men who feel self-conscious about their appearance, breast-reduction surgery can be helpful.
Before the operation
Rarely, the breast enlargement can be caused by medicines (for high blood pressure, heart disease and prostate cancer), drugs (such as marijuana and anabolic steroids), some diseases (such as liver failure and some cancers) and some very rare congenital abnormalities (errors of development that one is born with). These causes should be excluded by the surgeon during an initial consultation.
Additional information will be needed at this consultation regarding overall health, chest size and body shape, previous chest surgery, any bleeding tendencies and healing capabilities, some of which will be affected by smoking, alcohol and various medications.
A preoperative check-up is made according to the surgeon’s recommendations. You will meet the anesthesiologist in consultation at latest, 48 hours prior to surgery.
No medication containing aspirin will be taken for 10 days before surgery.
Hospital stay and type of anesthesia
Most operations for gynecomastia take about 1-2 hours to complete and are performed under general anesthesia. An overnight stay at the hospital is usually required.
The procedure
Techniques are adapted to every new case, in order to obtain the best possible results.. Some general principles involve:
The breast is made up of two main components, glandular tissue (firm and dense) and fatty tissue (soft). The ratio of glandular to fatty tissue in any breast varies from individual to individual and in gynecomastia there may be an excess of both.
If there is predominantly a diffuse fatty enlargement of the breast, liposuction is the usual treatment. This involves sucking out the tissue through a small tube inserted via a 3-4mm incision.
If excess glandular tissue is the primary cause of breast enlargement, it may need to be excised (cut out) with a scalpel. This will leave a scar, usually around the nipple edge. This excision can be performed alone or in conjunction with liposuction.
Major reductions that involve the removal of a significant amount of tissue and skin may require larger incisions that result in more obvious scars.
After the operation
Following the surgery the chest is swollen and bruised for a while and it can be difficult to assess the full effect of the operation. To help reduce swelling, patients are often instructed to wear an elastic pressure garment continuously for one or two weeks.
It is advisable to refrain from exercise for about three weeks and, in general, it takes about six weeks before one can return to completely normal activities.
Surgery involves coagulating of blood vessels and increased activity of any kind may open these vessels leading to a bleed, or hematoma. Activity that increases your pulse or heart rate may cause additional bruising, swelling, and the need for return to surgery and control bleeding. It is wise to refrain from intimate physical activities until your physician states it is safe.
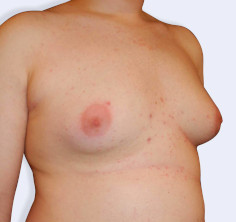
Picture Gallery
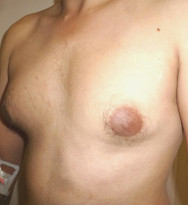
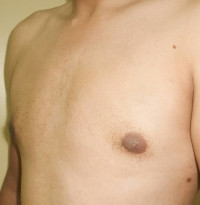
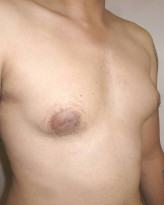
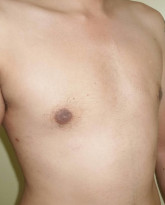
The result
Every patient is different, but most men notice improvement immediately after a male breast reduction procedure and continue to see improvement as the area heals over the course of a few weeks. The precise healing time however may vary and will depend on the technique used. To help facilitate healing, a compression garment is generally worn for a few days.
Male breast reduction can yield long-lasting, even permanent, results, improving the patient’s self-image and enhancing his self-confidence. However, before this final outcome, one should be patient, wait for scars to heal, and accept a regular follow-up during the first year.
Imperfect results
Good results are expected in most cases. However, occasionally the patient may be disappointed with the results of surgery due to:
- Asymmetry: differences in terms of breast and nipple shape, size, or symmetry
- Wound disruption
- Poor healing
- Loss of sensation may occur after surgery
- Unsatisfactory surgical scar location.
In some situations, it may not be possible to achieve optimal results with a single surgical procedure. It may be necessary to perform additional surgery to improve your results.
It is important that all patients seeking to undergo elective surgery have realistic expectations that focus on improvement rather than perfection
Possible complications
Gynecomastia surgery, even if performed for aesthetic reasons, is a genuine surgical procedure, with the consequent risks related to all medical acts. There are surgical and aesthetic complications. Concerning anesthesia, the anesthesiologist will inform you about all the anesthetic risks. You must be aware that anesthesia can sometimes cause unpredictable body reactions that can be difficult to control. The presence of an experienced anesthesiologist, in a surgical environment, means that the risks are statistically practically negligible.
The potential complications of the surgery are relatively rare. They include inadequate removal of breast tissue, an uneven contour to the chest and reduced nipple sensation. If an excision has been performed, rather than liposuction, then a blood clot can form that may need to be drained at a second operation.
Additional rare complications may include:
Fat Necrosis: Fatty tissue found deep in the skin might die. This may produce areas of firmness within the skin. Additional surgery to remove areas of fat necrosis may be necessary. There is the possibility of contour irregularities in the skin that may result from fat necrosis.
Seroma: Infrequently, fluid may accumulate between the skin and the underlying tissues following surgery, trauma or vigorous exercise. Should this problem occur, it may require additional procedures for drainage of fluid.
My Way …. “Metron Ariston”
Waterjet Assisted Liposuction (WAL) is the latest evolution in liposuction techniques and devices for body contouring and fat harvesting. Aesthetic satisfaction is considerably increased for patients who have undergone WAL Breast Reduction due to significant advantages over the open-surgical method, such as:
- Less complications
- Less scarring
- Faster recovery
- Less discomfort
- Lower cost
Waterjet Assisted Liposuction and/or Breast-reduction surgery can substantially help men regain their self-esteem and vitality, alleviate any emotional discomfort, and prevent potential limitations.
This webpage aims to provide some information about the subject. Individual patient circumstances may differ, which might alter both the advice and course of therapy given to you by your doctor.
Source:
American Society of Plastic Surgeons, British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons, French Society of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery
